ASCIS Qualification 2021
ASCIS Qualification 2021
Chào các anh em, toi là dr00py, cryptographer của UIT.W3 😃
khoe tí: team tui (UIT.W3) được đi final các anh em ạ he he he
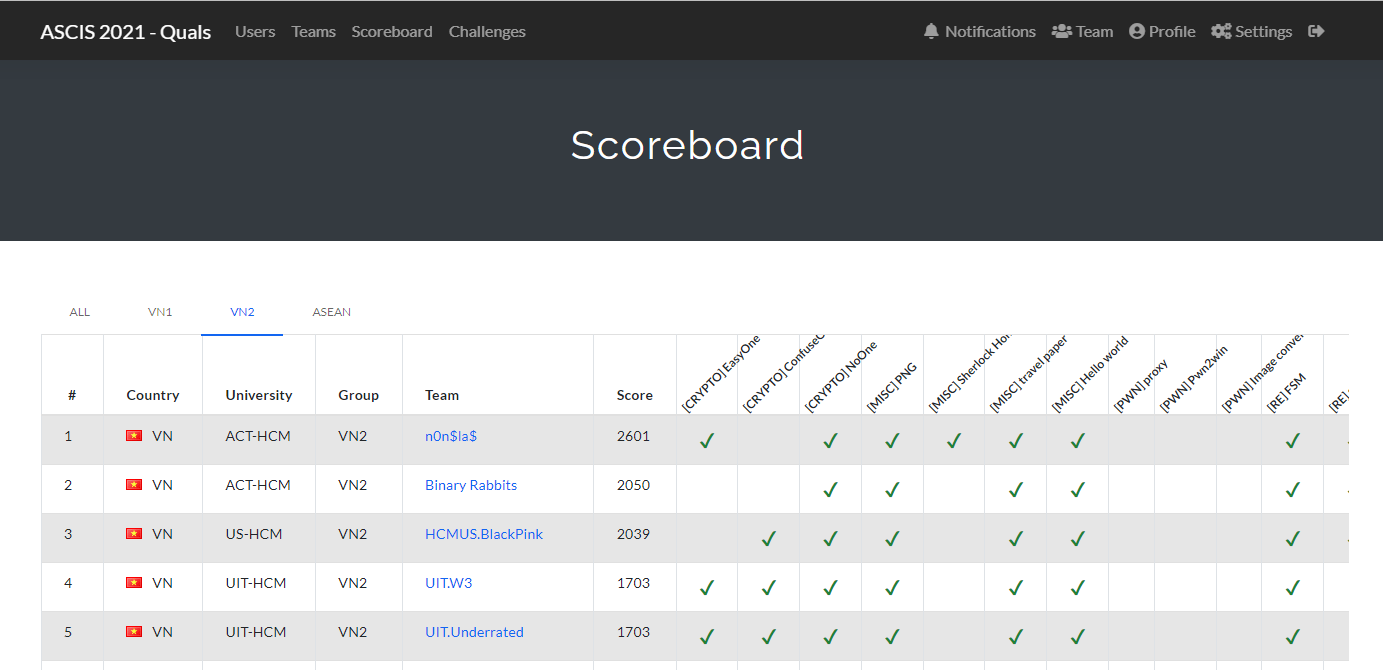
Đến bây giờ vẫn không biết BTC có up lộn đề crypto thành đề web không nữa .__. 🙄
Easyone (100pts)
http://139.180.213.39:8100/
He he cứ register rồi log acc vô bình thường 😀
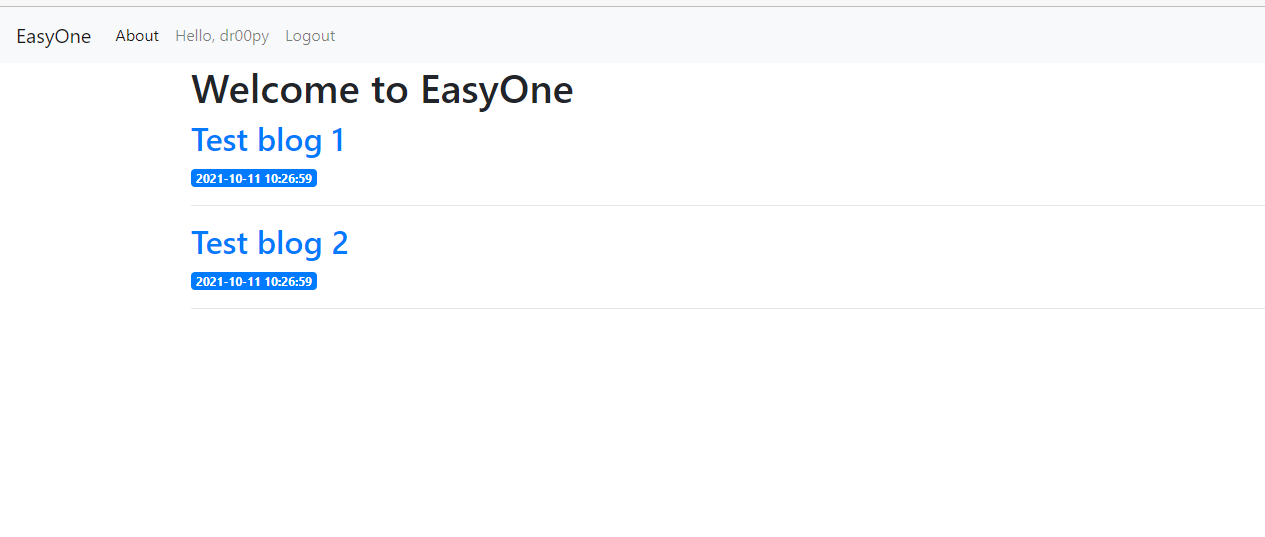
Ở góc trái trên, ngay chỗ Hello, <tên user>, khi mình bấm vào nó sẽ direct qua /flag, nhưng làm gì có vụ dễ vậy?
😃 bây giờ mình bấn loạn, bấm thử vô About xong nó hiện ra cái này:
Ô mình coi được source!!! Có hy vọng rồi, source này chia làm 2 phần:
app.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import base64
import hashlib
from logging import NullHandler, root
import sys
import os
from Crypto import Random
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from werkzeug.exceptions import abort
from functools import wraps
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, url_for, flash, redirect, session, make_response, g
import mysql.connector
import werkzeug
import ssl
import OpenSSL
from OpenSSL import crypto
from certutils import CertInfo, verify_certificate_chain
DB_HOST = os.getenv("MYSQL_HOST", "xxxxxx")
DB_USER = os.getenv("MYSQL_USER", "xxxxxx")
DB_PASS = os.getenv("MYSQL_PASSWORD", "xxxxxx")
DB_NAME = os.getenv("MYSQL_DATABASE", "xxxxxx")
def get_db_connection():
conn = mysql.connector.connect(host = DB_HOST, user = DB_USER, passwd = DB_PASS, database = DB_NAME, auth_plugin='mysql_native_password')
conn.autocommit = True
return conn
def get_post(post_id):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = %s',
(post_id,))
post = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
if post is None:
abort(404)
return post
def verify_login(username, password):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT id, username, password, email, role from users WHERE username = %s AND password = %s',
(username, password))
user = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
return user
def do_register(username, password, email, role):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('INSERT INTO users (username, password, email, role) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)',
(username, password, email, role))
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
def validate_certificate(file):
trusted_certs = ['./ca.crt', './app.crt']
for root_cert in trusted_certs:
if not os.path.isfile(root_cert):
raise Exception("Cannot found root certs")
clientcert = file.stream.read()
return verify_certificate_chain(clientcert, trusted_certs)
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
ROLE_ADMIN = 0
ROLE_USER = 1
def login_required(f):
@wraps(f)
def wrap(*args, **kwargs):
try:
if "username" not in session or session["username"] == "" or session["username"] is None:
abort(401)
print(session["username"])
except:
abort(401)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return wrap
@app.route("/index")
@login_required
def index():
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM posts')
posts = cur.fetchall()
cur.close()
conn.close()
return render_template('index.html', posts=posts)
@app.route("/flag")
@login_required
def flag():
flag = "You are not admin"
if session["role"] == ROLE_ADMIN:
flag = "ASCIS{xxxxxx}"
return render_template('flag.html', flag=flag)
@app.route('/<int:post_id>')
@login_required
def post(post_id):
post = get_post(post_id)
return render_template('post.html', post=post)
@app.route("/about")
@login_required
def about():
return render_template('about.html')
@app.route("/register", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
email = request.form['email']
role = ROLE_USER
if not username or not password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')
else:
do_register(username, password, email, role)
return redirect(url_for('login'))
return render_template('register.html')
@app.route("/", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
if not username or not password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')
else:
# verify login
user = verify_login(username, password)
if not user:
flash('Username and Password is not correct!')
else:
session["username"] = user[1]
session["role"] = user[4]
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('login.html')
# This function only for admin
@app.route("/logincert", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def logincert():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = None
uploaded_file = request.files['file']
if uploaded_file.filename != '':
split_tup = os.path.splitext(uploaded_file.filename)
if split_tup[1] != ".pem":
flash('Cert file is invalid')
return render_template('logincert.html')
else:
username = validate_certificate(uploaded_file)
if username is None:
flash('Login cert is invalid!')
return render_template('logincert.html')
else:
session["username"] = username
session["role"] = ROLE_ADMIN
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('logincert.html')
@app.route("/logout")
def logout():
session["username"] = None
session["role"] = None
session.clear()
return redirect(url_for('login'))
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8100, debug=False)
certutils.py
import base64
import hashlib
from logging import NullHandler, root
import sys
import os
from Crypto import Random
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from werkzeug.exceptions import abort
from functools import wraps
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, url_for, flash, redirect, session, make_response, g
import mysql.connector
import werkzeug
import ssl
import OpenSSL
from OpenSSL import crypto
import datetime
class CertInfo:
def __init__(
self,
cert=None,
):
self.cert = cert
def decode_x509name_obj(self, o):
parts = []
for c in o.get_components():
parts.append(c[0].decode('utf-8') + '=' + c[1].decode('utf-8'))
return ', '.join(parts)
def cert_date_to_gmt_date(self, d):
return datetime.datetime.strptime(d.decode('ascii'), '%Y%m%d%H%M%SZ')
def cert_date_to_gmt_date_string(self, d):
return self.cert_date_to_gmt_date(d).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S GMT")
def get_item(self, item, extension=None, return_as=None, algo=None):
try:
if item == 'subject':
return self.decode_x509name_obj(self.cert.get_subject())
elif item == 'subject_o':
return self.cert.get_subject().O.strip()
elif item == 'subject_cn':
return self.cert.get_subject().CN.strip()
elif item == 'extensions':
ext_count = self.cert.get_extension_count()
if extension is None:
ext_infos = []
for i in range (0, ext_count):
ext = self.cert.get_extension(i)
ext_infos.append(ext.get_short_name().decode('utf-8'))
return ext_infos
for i in range (0, ext_count):
ext = self.cert.get_extension(i)
if extension in str(ext.get_short_name()):
return ext.__str__().strip()
return None
elif item == 'version':
return self.cert.get_version()
elif item == 'pubkey_type':
pk_type = self.cert.get_pubkey().type()
if pk_type == crypto.TYPE_RSA:
return 'RSA'
elif pk_type == crypto.TYPE_DSA:
return 'DSA'
return 'Unknown'
elif item == 'pubkey_pem':
return crypto.dump_publickey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, self.cert.get_pubkey()).decode('utf-8')
elif item == 'serial_number':
return self.cert.get_serial_number()
elif item == 'not_before':
not_before = self.cert.get_notBefore()
if return_as == 'string':
return self.cert_date_to_gmt_date_string(not_before)
return self.cert_date_to_gmt_date(not_before)
elif item == 'not_after':
not_after = self.cert.get_notAfter()
if return_as == 'string':
return self.cert_date_to_gmt_date_string(not_after)
return self.cert_date_to_gmt_date(not_after)
elif item == 'has_expired':
return self.cert.has_expired()
elif item == 'issuer':
return self.decode_x509name_obj(self.cert.get_issuer())
elif item == 'issuer_o':
return self.cert.get_issuer().O.strip()
elif item == 'issuer_cn':
return self.cert.get_issuer().CN.strip()
elif item == 'signature_algorithm':
return self.cert.get_signature_algorithm().decode('utf-8')
elif item == 'digest':
# ['md5', 'sha1', 'sha256', 'sha512']
return self.cert.digest(algo)
elif item == 'pem':
return crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, self.cert).decode('utf-8')
else:
return None
except Exception as e:
# logger.error('item = {}, exception, e = {}'.format(item, e))
return None
@property
def subject(self):
return self.get_item('subject')
@property
def subject_o(self):
return self.get_item('subject_o')
@property
def subject_cn(self):
return self.get_item('subject_cn')
@property
def subject_name_hash(self):
return self.get_item('subject_name_hash')
@property
def extension_count(self):
return self.get_item('extension_count')
@property
def extensions(self):
return self.get_item('extensions')
@property
def extension_basic_constraints(self):
return self.get_item('extensions', extension='basicConstraints')
@property
def extension_subject_key_identifier(self):
return self.get_item('extensions', extension='subjectKeyIdentifier')
@property
def extension_authority_key_identifier(self):
return self.get_item('extensions', extension='authorityKeyIdentifier')
@property
def extension_subject_alt_name(self):
return self.get_item('extensions', extension='subjectAltName')
@property
def version(self):
return self.get_item('version')
@property
def pubkey_type(self):
return self.get_item('pubkey_type')
@property
def pubkey_pem(self):
return self.get_item('pubkey_pem')
@property
def serial_number(self):
return self.get_item('serial_number')
@property
def not_before(self):
return self.get_item('not_before')
@property
def not_before_s(self):
return self.get_item('not_before', return_as='string')
@property
def not_after(self):
return self.get_item('not_after')
@property
def not_after_s(self):
return self.get_item('not_after', return_as='string')
@property
def has_expired(self):
return self.get_item('has_expired')
@property
def issuer(self):
return self.get_item('issuer')
@property
def issuer_o(self):
return self.get_item('issuer_o')
@property
def issuer_cn(self):
return self.get_item('issuer_cn')
@property
def signature_algorithm(self):
return self.get_item('signature_algorithm')
@property
def digest_sha256(self):
return self.get_item('digest', algo='sha256')
@property
def pem(self):
return self.get_item('pem')
def verify_certificate_chain(cert_pem, trusted_certs):
certificate = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cert_pem)
# parse ceritificate information
clientcert = CertInfo(certificate)
# get subject common name
subject = clientcert.subject_cn
issuer = clientcert.issuer_cn
# Check if subject is admin user
if subject != "admin":
raise Exception("Not trusted user")
# validate issuer
if issuer != "ca":
raise Exception("Not trusted ca")
thumbprint = clientcert.digest_sha256.decode('utf-8')
#TODO: validate thumbprint
#Create a certificate store and add your trusted certs
try:
store = crypto.X509Store()
# Assuming the certificates are in PEM format in a trusted_certs list
for _cert in trusted_certs:
cert_file = open(_cert, 'r')
cert_data = cert_file.read()
client_certificate = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cert_data)
store.add_cert(client_certificate)
# Create a certificate context using the store
store_ctx = crypto.X509StoreContext(store, certificate)
# Verify the certificate signature, returns None if it can validate the certificate
store_ctx.verify_certificate()
# verify success
return subject
except Exception as e:
print("[+] Debug certificate validation failed")
return False
Thật sự là mình ngu vụ web này cực, nhưng mà cũng ráng đọc, tại vì team cũng đang cố gắng!!! Sau 1 thời gian mình thấy chỗ này
ở trong file app.py
# This function only for admin
@app.route("/logincert", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def logincert():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = None
uploaded_file = request.files['file']
if uploaded_file.filename != '':
split_tup = os.path.splitext(uploaded_file.filename)
if split_tup[1] != ".pem":
flash('Cert file is invalid')
return render_template('logincert.html')
else:
username = validate_certificate(uploaded_file)
if username is None:
flash('Login cert is invalid!')
return render_template('logincert.html')
else:
session["username"] = username
session["role"] = ROLE_ADMIN
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('logincert.html')
À có route qua /logincert kìa, mình xem thử, chắc chắc đó là chỗ up file .pem để authencatic 🤔
Rồi oke, mình xác định được thứ cần làm rồi! nhưng ở function trên, username trên sẽ đưa vào function validate_certificate(uploaded_file) với uploaded_file là file .pem post lên! Và mình xem qua hàm validate_certificate(uploaded_file) thử:
def validate_certificate(file):
trusted_certs = ['./ca.crt', './app.crt']
for root_cert in trusted_certs:
if not os.path.isfile(root_cert):
raise Exception("Cannot found root certs")
clientcert = file.stream.read()
return verify_certificate_chain(clientcert, trusted_certs)
Thật căng thẳng vì mình chưa từng tiếp xúc sâu vào PEM file bao giờ. Hàm trên để check trusted certificate thôi à. Các anh em muốn xem thì ở link này. Sau đó direct qua hàm verify_certificate_chain(clientcert, trusted_certs) ở file certutils.py
def verify_certificate_chain(cert_pem, trusted_certs):
certificate = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cert_pem)
# parse ceritificate information
clientcert = CertInfo(certificate)
# get subject common name
subject = clientcert.subject_cn
issuer = clientcert.issuer_cn
# Check if subject is admin user
if subject != "admin":
raise Exception("Not trusted user")
# validate issuer
if issuer != "ca":
raise Exception("Not trusted ca")
thumbprint = clientcert.digest_sha256.decode('utf-8')
#TODO: validate thumbprint
#Create a certificate store and add your trusted certs
try:
store = crypto.X509Store()
# Assuming the certificates are in PEM format in a trusted_certs list
for _cert in trusted_certs:
cert_file = open(_cert, 'r')
cert_data = cert_file.read()
client_certificate = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cert_data)
store.add_cert(client_certificate)
# Create a certificate context using the store
store_ctx = crypto.X509StoreContext(store, certificate)
# Verify the certificate signature, returns None if it can validate the certificate
store_ctx.verify_certificate()
# verify success
return subject
except Exception as e:
print("[+] Debug certificate validation failed")
return False
Phân tích mode on:
- Nè ban đầu nó đưa file mình vô để analyze gì đó, nói chung là để lấy lại các thuộc tính trước khi decrypt. Trong đó có nhiều thuộc tính, đại loại như: C, O, OU, ST, CN, datetime,… Vì mình debug file này rồi, nên các anh em muốn thử thì vào link này để gen 1 file
pemra import vô file chạy thử nè 😥
-
Để ý nè, nếu sau khi analyze ra,
subject = "admin"vàissuer = "ca"thì mình bypass được challenge này luôn!. -
Bây giờ mình xem thử subject và issuer là bằng gì? Lướt xem lại code, mình xác định được subject = clientcert.subject_cn =
self.cert.get_subject().CN.strip() (ở class), còn issuer = clientcert.issuer_cn =self.cert.get_issuer().CN.strip() (ở class)
Warning: khi mà generate file ‘.pem’ ở đâu thì mạc định 2 thứ đó sẽ như nhau? Đúng vậy! Vì đây là self-signed, nên là issuer luôn là subject. Sau khoảng hơn 1h mình debug để cố gắng sửa issuer = “ca” thì đã rã rời sau khi tìm được tài liệu nói trên đó. Vì thế mình phải tự gen file pem ra…
- Link này là cứu tinh của mình, khi mà nó chỉ cách gen file bằng python. Vậy là nếu mình control được code thì mình có thể thay đổi theo ý mình! Đúng vậy, mình đem hết cả về để run step-by-step để hiểu code. Sau đó mình sửa theo ý của mình: nghĩa là mình sẽ thay
issuer = "ca"lại thay vì là để nó bằng subject! Mình đưa nó thành 1 trường mới, để gen chính xác hơn. Cụ thể ở 2 files sau:
pki_helpers.py
# pki_helpers.py
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.x509.oid import NameOID
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
def generate_public_key(private_key, filename, **kwargs):
subject = x509.Name(
[
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COUNTRY_NAME, kwargs["country"]),
x509.NameAttribute(
NameOID.STATE_OR_PROVINCE_NAME, kwargs["state"]
),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.LOCALITY_NAME, kwargs["locality"]),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.ORGANIZATION_NAME, kwargs["org"]),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COMMON_NAME, kwargs["hostname"]),
]
)
issuer = x509.Name(
[
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COUNTRY_NAME, kwargs["country"]),
x509.NameAttribute(
NameOID.STATE_OR_PROVINCE_NAME, kwargs["state"]
),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.LOCALITY_NAME, kwargs["locality"]),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.ORGANIZATION_NAME, kwargs["org"]),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COMMON_NAME, "ca"),
]
)
# This certificate is valid from now until 30 days
valid_from = datetime.utcnow()
valid_to = valid_from + timedelta(days=30)
# Used to build the certificate
builder = (
x509.CertificateBuilder()
.subject_name(subject)
.issuer_name(issuer)
.public_key(private_key.public_key())
.serial_number(x509.random_serial_number())
.not_valid_before(valid_from)
.not_valid_after(valid_to)
.add_extension(x509.BasicConstraints(ca=True,
path_length=None), critical=True)
)
# Sign the certificate with the private key
public_key = builder.sign(
private_key, hashes.SHA256(), default_backend()
)
with open(filename, "wb") as certfile:
certfile.write(public_key.public_bytes(serialization.Encoding.PEM))
return public_key
from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import rsa
def generate_private_key(filename: str, passphrase: str):
private_key = rsa.generate_private_key(
public_exponent=65537, key_size=2048, backend=default_backend()
)
utf8_pass = passphrase.encode("utf-8")
algorithm = serialization.BestAvailableEncryption(utf8_pass)
with open(filename, "wb") as keyfile:
keyfile.write(
private_key.private_bytes(
encoding=serialization.Encoding.PEM,
format=serialization.PrivateFormat.TraditionalOpenSSL,
encryption_algorithm=algorithm,
)
)
return private_key
gen.py
from pki_helpers import generate_private_key, generate_public_key
private_key = generate_private_key("ca-private-key.pem", "secret_password")
print(private_key)
generate_public_key(private_key, filename="ca-public-key.pem", country="US", state="Maryland", locality="Baltimore", org="My CA Company", hostname="admin",)
- Mình lấy file
.pemnày vào debug thử file của mình sau khi chỉnh sửa 1 loạt. Ô, qua được hết 😁😁😁, thế là mình up lên server luôn cho nóng!!!
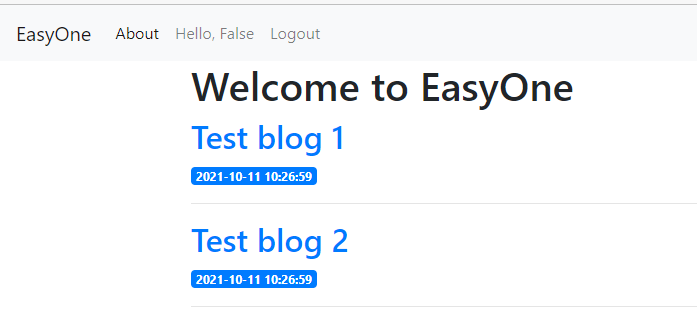
Ơ tên đổi thành Hello, False, rén vl, nhưng mà mình có cảm giác thành công rồi 😘. Bấm vô thử:
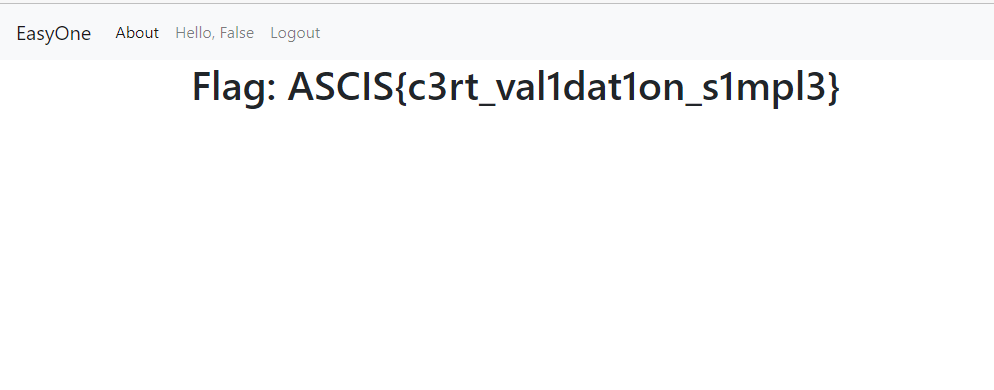
Nước mắt anh rơi, trò chơi kết thúc.
1 it comment: bài này tốn nhiều thời gian vl, nhưng mà mình mài đít đọc được file pem là gì, ca như nào,… Thôi thì thành quả cũng đáng nhỉ 🤗
Noone (100pts)
http://139.180.213.39:8300/
Bài này nhiều đội solve nhất trong mảng crypto (37).
Flashback lại bài trước, các bước tương tự để coi lại source, tui lười ghi lại quá đi 😑
app.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import base64
import hashlib
import sys
import os
from Crypto import Random
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from werkzeug.exceptions import abort
from functools import wraps
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, url_for, flash, redirect, session, make_response, g
import mysql.connector
DB_HOST = os.getenv("MYSQL_HOST", "xxxxxxx")
DB_USER = os.getenv("MYSQL_USER", "xxxxxxx")
DB_PASS = os.getenv("MYSQL_PASSWORD", "xxxxxxx")
DB_NAME = os.getenv("MYSQL_DATABASE", "xxxxxxx")
# input: bytes, output: base64 text
def encrypt(plainbytes, key):
iv = Random.new().read(AES.block_size)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
cipherbytes = cipher.encrypt(plainbytes)
ciphertext = base64.b64encode(iv + cipherbytes)
return ciphertext
# input: base64 text, output: bytes
def decrypt(ciphertext, key):
cipherbytes = base64.b64decode(ciphertext)
iv = cipherbytes[:AES.block_size]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
plainbytes = cipher.decrypt(cipherbytes[AES.block_size:])
return plainbytes
def get_db_connection():
conn = mysql.connector.connect(host = DB_HOST, user = DB_USER, passwd = DB_PASS, database = DB_NAME, auth_plugin='mysql_native_password')
conn.autocommit = True
return conn
def get_post(post_id):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = %s',
(post_id,))
post = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
if post is None:
abort(404)
return post
def verify_login(username, password):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT id, username, password, email, encryptkey, role from users WHERE username = %s AND password = %s',
(username, password))
user = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
return user
def do_register(username, password, email, role):
key = base64.b64encode(Random.new().read(AES.block_size))
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('INSERT INTO users (username, password, email, role, encryptkey ) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)',
(username, password, email, role, key))
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
def get_encryptkey(userid):
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT encryptkey from users WHERE id = %s',
(userid, ))
user = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
return base64.b64decode(user[0])
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
ROLE_ADMIN = 0
ROLE_USER = 1
def login_required(f):
@wraps(f)
def wrap(*args, **kwargs):
try:
ciphertext = request.cookies.get('authtoken')
userid = request.cookies.get('userid')
if not ciphertext or not userid:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
encryptkey = get_encryptkey(userid)
plainbytes = decrypt(ciphertext, encryptkey)
usernamelen = int.from_bytes(plainbytes[:2], "little")
usernameencoded = plainbytes[2:usernamelen+2]
username = usernameencoded.decode("utf-8")
role = plainbytes[usernamelen+2]
g.username = username
g.role = role
except:
abort(401)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return wrap
@app.route("/index")
@login_required
def index():
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM posts')
posts = cur.fetchall()
cur.close()
conn.close()
return render_template('index.html', posts=posts)
@app.route("/flag")
@login_required
def flag():
flag = "You are not admin"
if g.role == ROLE_ADMIN:
flag = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
return render_template('flag.html', flag=flag)
@app.route('/<int:post_id>')
@login_required
def post(post_id):
post = get_post(post_id)
return render_template('post.html', post=post)
@app.route("/about")
@login_required
def about():
return render_template('about.html')
@app.route("/register", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
email = request.form['email']
role = ROLE_USER
if not username or not password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')
else:
do_register(username, password, email, role)
return redirect(url_for('login'))
return render_template('register.html')
@app.route("/", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
if not username or not password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')
else:
# verify login
user = verify_login(username, password)
if not user:
flash('Username and Password is not correct!')
else:
userid = user[0]
username = user[1]
role = user[5]
# get key
key = base64.b64decode(user[4])
# create authtoken
usernamebytes = username.encode('utf-8')
usernamelen = len(usernamebytes)
plainbytes = len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2, "little") + usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1, "little")
ciphertext = encrypt(plainbytes, key)
response = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')))
response.set_cookie('userid', str(userid))
response.set_cookie('authtoken', ciphertext)
return response
return render_template('login.html')
@app.route("/logout")
def logout():
response = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')))
response.set_cookie('userid', '0', expires=0)
response.set_cookie('authtoken', '', expires=0)
return response
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8080, debug=False)
Sau khi biết 1 chút đỉnh về web run rồi, mình ngó thẳng vào flag:
@app.route("/flag")
@login_required
def flag():
flag = "You are not admin"
if g.role == ROLE_ADMIN:
flag = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
return render_template('flag.html', flag=flag)
Mục đích lại rất đơn giản: đưa mình thành admin. Còn làm như nào thì chưa biết 😥
Ok giờ xem mấy function nào: À đây rồi, phần login
@app.route("/", methods=('GET', 'POST'))
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
if not username or not password:
flash('Username and Password is required!')
else:
# verify login
user = verify_login(username, password)
if not user:
flash('Username and Password is not correct!')
else:
userid = user[0]
username = user[1]
role = user[5]
# get key
key = base64.b64decode(user[4])
# create authtoken
usernamebytes = username.encode('utf-8')
usernamelen = len(usernamebytes)
plainbytes = len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2, "little") + usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1, "little")
ciphertext = encrypt(plainbytes, key)
response = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')))
response.set_cookie('userid', str(userid))
response.set_cookie('authtoken', ciphertext)
return response
return render_template('login.html')
Rõ ràng lúc login, không chỉ nó verify acc của mình, nó còn lấy thông tin mình làm gì nữa kìaaaaa
À, nó lụm plaintext để decrypt, xong rồi set authtoken 🙂. Vậy bây giờ mình xem phần ciphertext = encrypt(plainbytes, key) thôi. À mà key là gì đó nó lưu trong db của server, chắc là gen random 😶 nên mình không đoán được đâu.
def encrypt(plainbytes, key):
iv = Random.new().read(AES.block_size)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
cipherbytes = cipher.encrypt(plainbytes)
ciphertext = base64.b64encode(iv + cipherbytes)
return ciphertext
Vơn, quá ngắn gọn, mà càng ngắn càng nguy hiểm, xem sơ qua nào. Hê, đây là AES mode CFB với iv được random, sau khi encrypt, kết quả được trả về là iv + ciphertext đã được encode bằng base64. Vậy nghĩa là mình lụm authtoken về, sau đó là lấy được iv và cipher text ngay!.
- Plaintext phải có độ dài là bội của 16. nhìn vào plainbytes ở function trên-trên, thấy là len(username) chỉ lấy 2 bytes, role lấy 1 bytes, vậy giờ mình TẠO ACCOUNT MỚI có độ dài là 13 là ngon (vì cộng vào là 16). Sau khi dăng nhập, mình lấy được iv và cipher lần lượt là 16 kí tự đầu, và 16 kí tự cuối của cipher.
- Sau đây mình mô tả cái
AES mode CFB:
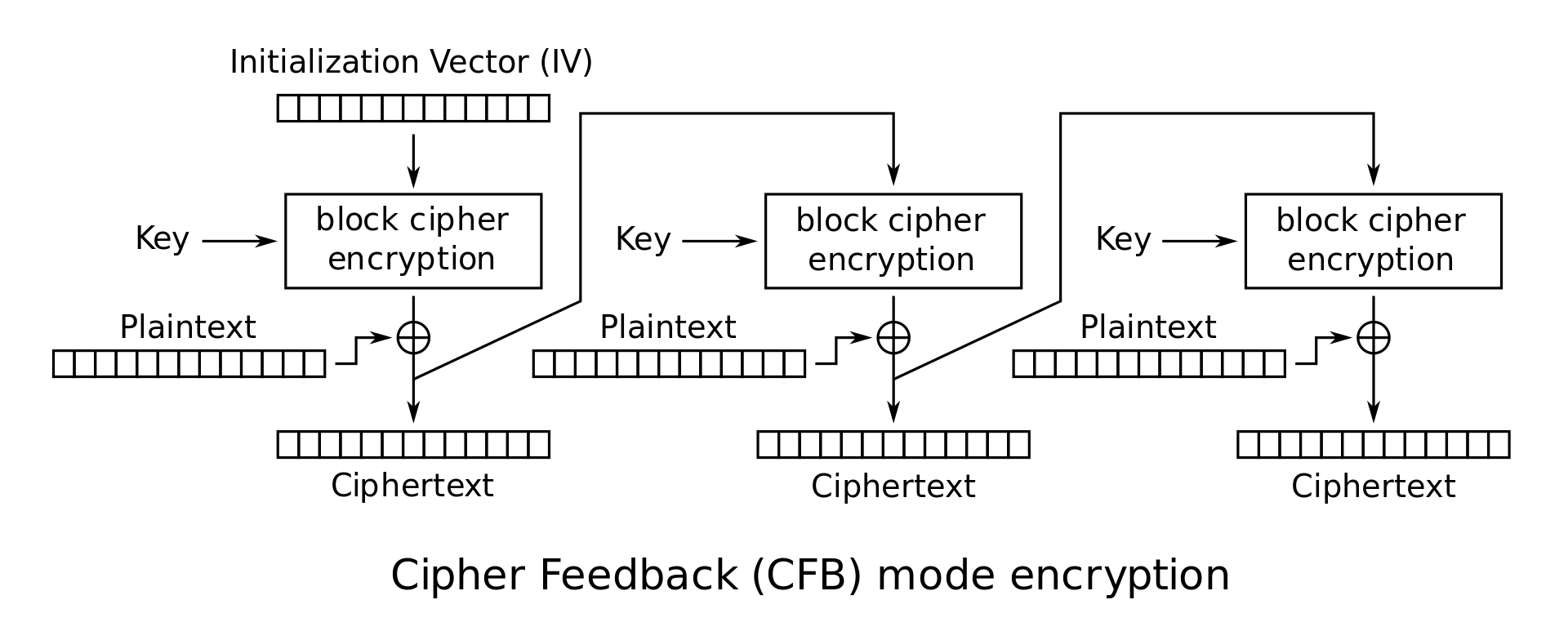
- iv vô 1 loạt xử lí phức tạp của AES, xong xor plaintext block đầu ra được cipher block đầu, còn về sau mình không thèm tính nữa. Vì plaintext của mình đúng 16 kí tự như đã giải thích trên nên chỉ quan tâm block đầu.
- Minh dùng cipher ^ plain(cái này mình biết) ^ plain(mình muốn tạo) thì sẽ cho ra cipher mới mình cần thay đổi.
- Sau đó mình sửa lại trong authtoken và F5 lại:
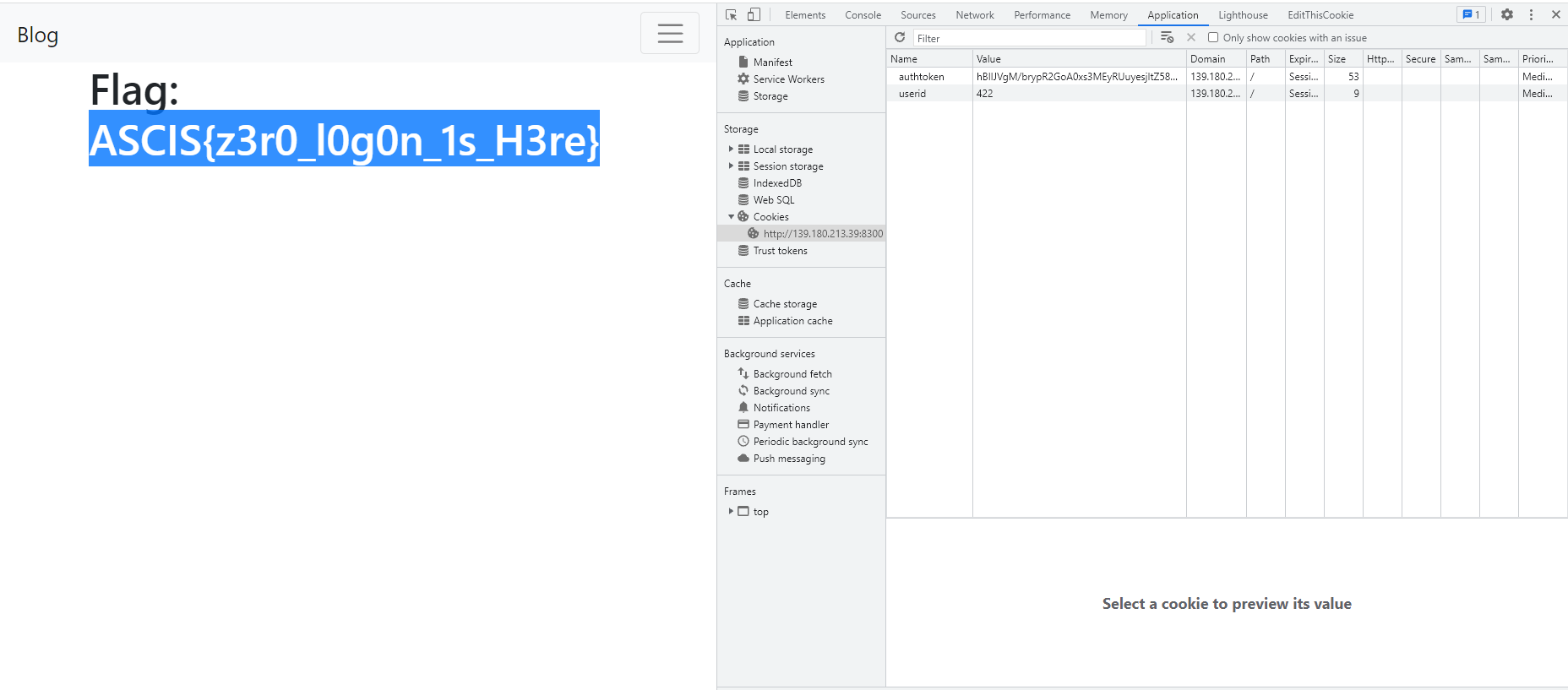
- Ý tưởng là vậy, nhưng để các anh em muốn solve lại thì nhiều thứ sẽ thay đổi theo session. Code mình bỏ đây, anh em thay số liệu nhé hehe
solve.py
import base64
import hashlib
from Crypto import Random
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import binascii
def xor(var, key):
return bytes(a ^ b for a, b in zip(var, key))
def encrypt(plainbytes, key):
iv = Random.new().read(AES.block_size)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
cipherbytes = cipher.encrypt(plainbytes)
ciphertext = base64.b64encode(iv + cipherbytes)
return ciphertext
# input: base64 text, output: bytes
def decrypt(ciphertext, key):
cipherbytes = base64.b64decode(ciphertext)
iv = cipherbytes[:AES.block_size]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
plainbytes = cipher.decrypt(cipherbytes[AES.block_size:])
return plainbytes
user = [422, "dr00py1234567", "dr00py", "dr00py1@gmail.com", b'ZG9hbmFuaGR1bmcxMjM0NQ==', 1]
userid = user[0]
username = user[1]
role = user[5]
key = base64.b64decode(user[4])
usernamebytes = username.encode('utf-8')
usernamelen = len(usernamebytes)
plainbytes = len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2, "little") + usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(1, "little")
#plainbytes1 = len(usernamebytes).to_bytes(2, "little") + usernamebytes + role.to_bytes(0, "little")
plainbytes1 = b'\r\x00dr00py1234567\x00'
authtoken = "hBlIJVgM/brypR2GoA0xs3MEyRUuyesjltZ58mkVaNI="
tokenarray = base64.b64decode(authtoken)
iv = tokenarray[:16]
cipherbytes = tokenarray[16:]
print("iv =", iv)
print("cipher =", cipherbytes)
new_cipher = xor(xor(plainbytes, cipherbytes), plainbytes1)
print("cipher =", new_cipher)
print(base64.b64encode(iv+new_cipher))
# thay cookie => solve
Khò khòoooooo
ConfuseOne (464pts)
http://139.180.213.39/
Bài này thật sự cảm ơn anh @dtro20 trong team mình rất nhiều 🥰. Khai sáng quá nhiều thứ luôn.

-> Nhìn vào mình chả có ý tưởng gì cả, chỉ reg acc rồi login vô ngồi nhìn thôi. Nhưng?
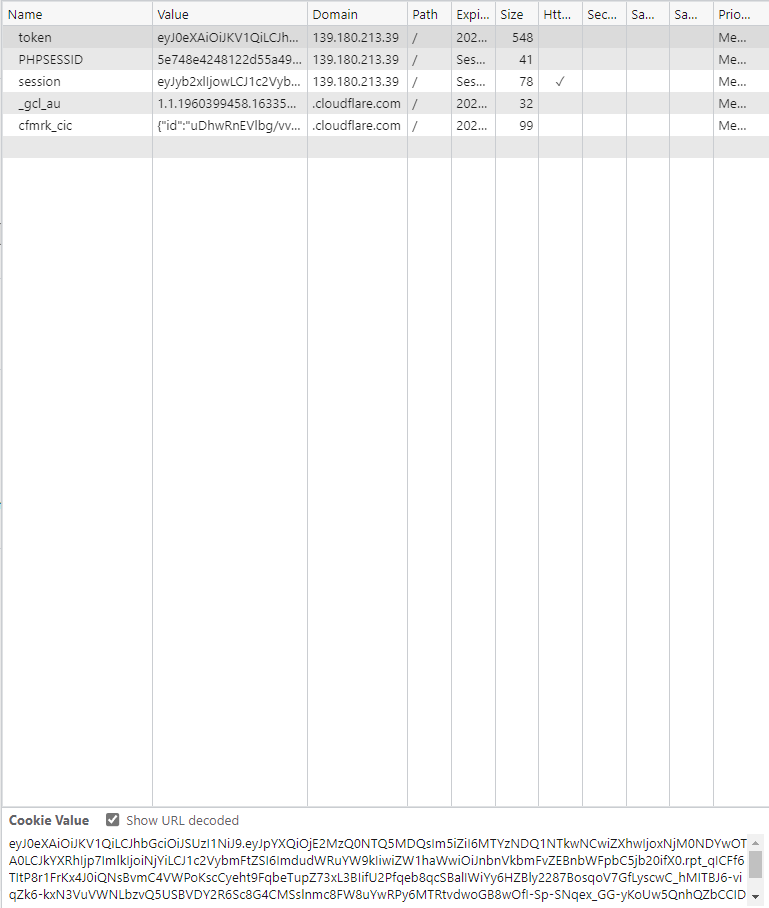
Token của nó là dạng JWT, và bài này chắc là JWT rs256!
Follow theo write-up này. Để có hướng giải nè. Rất đầy đủ và chi tiết.
Sau đó thay authtoken vào thôi
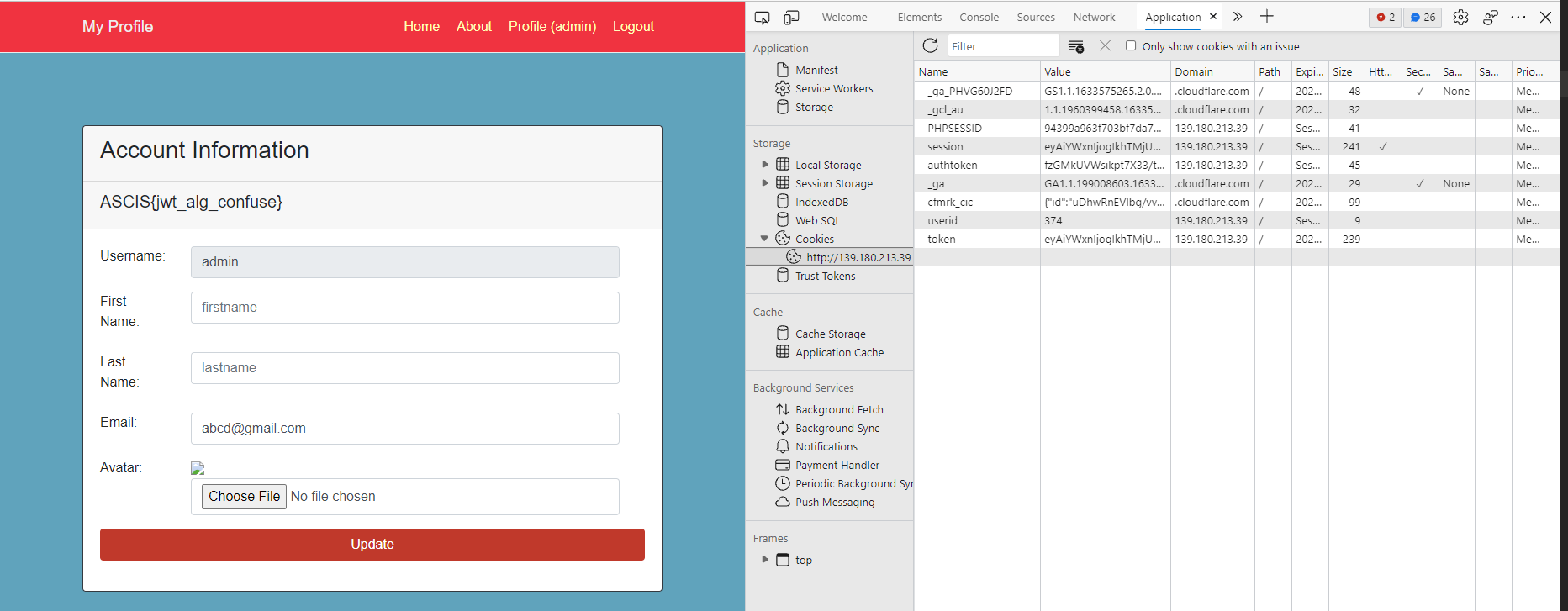
Quá kinh khủng? Đề web hay là crypto vậy ạ? Cám ơn mn đã đọc tới đây :(((